Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Gastroenteritis is a condition that affects the stomach and intestines, leading to uncomfortable symptoms like vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps. It’s often referred to as the “stomach flu,” though it’s not related to the seasonal flu. Knowing the key signs of gastroenteritis can help you recognize the symptoms early and prevent further complications. In this article, we’ll dive deeper into the key signs of gastroenteritis, its causes, prevention strategies, and what to do when you encounter these symptoms.
1. What is Gastroenteritis?
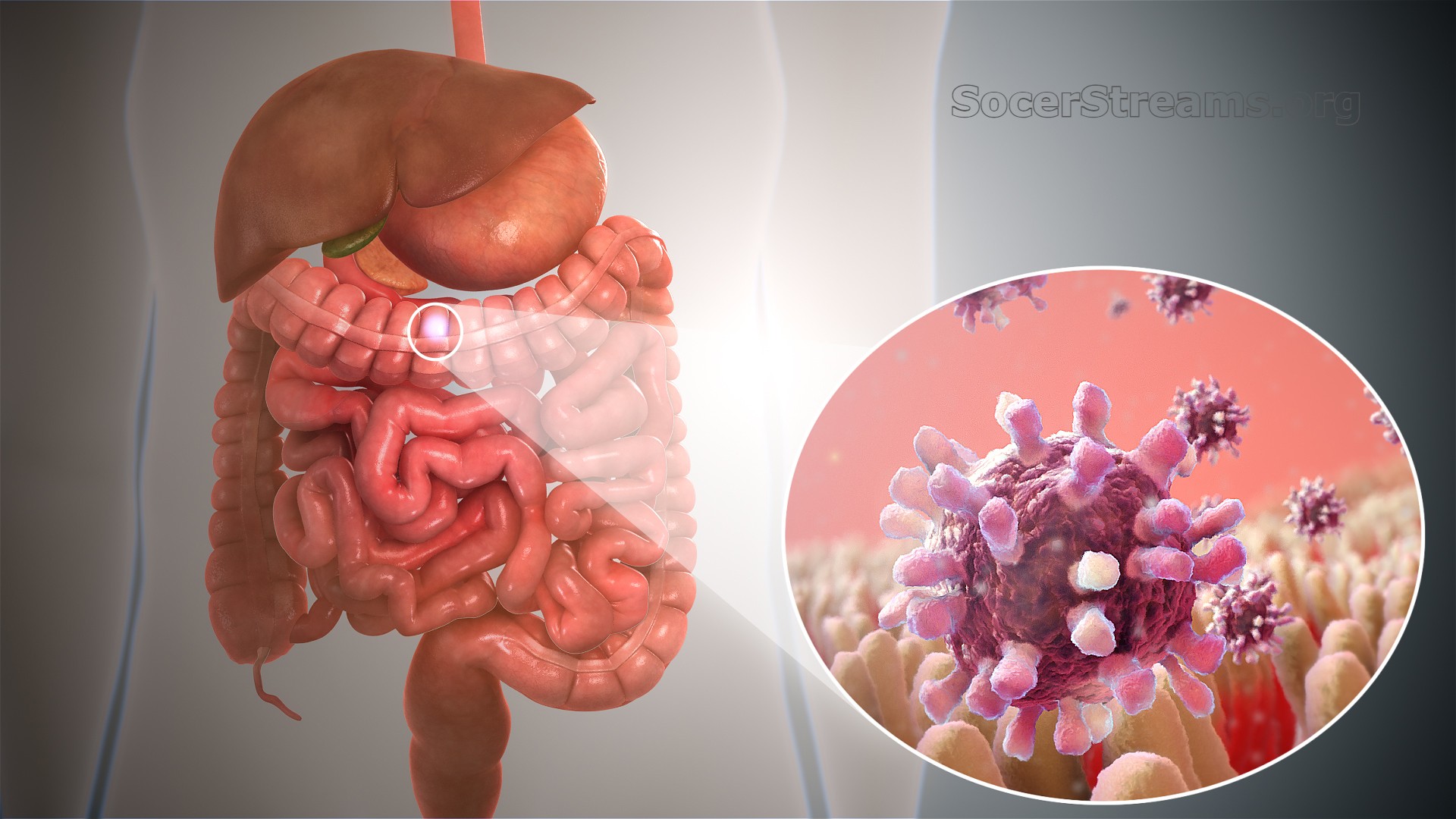
Gastroenteritis is the inflammation of the stomach and intestines. It is caused by infections from viruses, bacteria, or parasites. The condition leads to symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and fever. While it is often mild, it can cause severe dehydration if left untreated.
2. Common Causes of Gastroenteritis
Understanding the causes of gastroenteritis can help in preventing it. The most common cause is viral infection, especially norovirus, and rotavirus. Bacteria like Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter can also lead to gastroenteritis, typically through contaminated food or water.
3. Key Sign: Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea is usually the first sign that something is wrong with your stomach. It can quickly lead to vomiting, as your body attempts to eliminate the infection. Vomiting can occur in waves and may last for several hours to a day. This is a classic indicator of gastroenteritis.
4. Diarrhea: A Major Symptom
Diarrhea is another hallmark sign of gastroenteritis. It occurs as the body tries to expel harmful substances from the intestines. The diarrhea is usually watery and frequent, often coming in sudden urges that are hard to control.
5. Abdominal Pain and Cramps
Abdominal discomfort is commonly experienced during gastroenteritis. This includes cramps, bloating, and sharp, stabbing pains in the stomach. The pain usually intensifies after eating or drinking, as the stomach and intestines try to process food while inflamed.
6. Fever and Chills
In some cases, gastroenteritis can cause a mild fever, which is the body’s natural response to infection. Chills may accompany the fever as the body works to fight off the virus or bacteria. A mild fever may last for 24 to 48 hours before subsiding.
7. Dehydration Risk from Gastroenteritis
Dehydration is one of the most concerning risks of gastroenteritis. Due to diarrhea and vomiting, your body loses a significant amount of fluids and electrolytes. Dehydration can lead to dizziness, dry mouth, and fatigue. It’s important to stay hydrated by drinking fluids like water, electrolyte drinks, or clear broths.
8. Headaches and Muscle Aches
In addition to gastrointestinal symptoms, many people experience headaches and muscle aches. These symptoms are a result of the body’s immune response to the infection. Headaches may worsen as dehydration sets in, which is why staying hydrated is crucial.
9. Fatigue and Weakness
The body requires energy to fight off the infection causing gastroenteritis, leading to feelings of weakness and fatigue. This can make it difficult to engage in normal activities. Rest is essential, as it allows the body to recover.
10. How Long Does Gastroenteritis Last?
Most cases of gastroenteritis resolve within a few days. Symptoms typically last between 1 to 3 days, but in some cases, it can last up to a week. The duration depends on the cause, with viral infections usually resolving more quickly than bacterial infections.
11. When to See a Doctor for Gastroenteritis
While most cases of gastroenteritis resolve on their own, it’s essential to see a doctor if you experience severe symptoms. This includes prolonged vomiting or diarrhea lasting more than 3 days, high fever, or signs of dehydration like dark urine, dizziness, and excessive weakness. Infants, elderly individuals, and those with weakened immune systems should seek medical attention promptly.
12. How to Prevent Gastroenteritis
Preventing gastroenteritis largely relies on hygiene and food safety. Wash your hands frequently, especially after using the bathroom and before preparing or eating food. Be cautious when consuming raw or undercooked food, and avoid drinking unfiltered or contaminated water. If traveling to areas with limited sanitation, always opt for bottled water and avoid street food.
13. Treatment Options for Gastroenteritis
There is no specific cure for gastroenteritis, but treatment mainly involves managing the symptoms. Rest, hydration, and electrolyte replenishment are critical for recovery. In some cases, over-the-counter medications for nausea or diarrhea may help. Antibiotics may be prescribed if a bacterial infection is identified.
14. The Importance of Rest in Recovery
Getting plenty of rest is vital to help your immune system fight the infection. While you may feel weak and tired, rest allows your body to recover more quickly. Avoid strenuous physical activity until you feel better.
15. Diet Tips During Gastroenteritis
During recovery, it’s important to stick to bland, easy-to-digest foods. The BRAT diet (bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast) is often recommended. Avoid fatty, spicy, or dairy foods, as they may aggravate the stomach and delay recovery.
16. Long-Term Effects of Gastroenteritis
In most cases, gastroenteritis doesn’t cause long-term effects. However, recurring episodes of gastroenteritis can lead to chronic digestive issues. It’s essential to identify any underlying causes, especially if symptoms keep reappearing. If you’re frequently suffering from gastroenteritis, consult your doctor for further evaluation.
Conclusion
Gastroenteritis is a common, yet uncomfortable, condition that can cause various symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. Early recognition of these key signs can help you take the necessary steps to manage the condition effectively. While most cases are mild and self-limiting, it’s essential to stay hydrated and rest for a quick recovery. Preventive measures, like proper hygiene and food safety, are crucial in reducing your risk of infection. If symptoms persist or worsen, it’s important to seek medical advice. Stay informed, stay healthy, and take proactive steps to protect yourself and your loved ones from gastroenteritis.







